UV resin has become an essential material in a wide range of industries due to its fast curing times, superior performance, and versatility. However, with different applications requiring specific performance characteristics, choosing the right UV resin is crucial for achieving optimal results.
In this article, we'll explore the UV resin needs of different industries, the differences between soft and hard UV resins, and the use of UV resins in high-end applications like 3D printing and medical devices.

In the automotive industry, UV resins are primarily used for coatings, adhesives, and sealing applications. The resin must exhibit strong adhesion to various substrates, including metals, plastics, and composites. Automotive applications require UV resins that offer excellent durability, resistance to UV radiation, chemicals, and abrasion. For coatings, the resin must provide a glossy, high-quality finish, while adhesives must have strong bonding capabilities to withstand the demands of temperature and environmental exposure.
In the electronics industry, UV resins are used for coatings, encapsulation, and potting. These resins must possess good electrical insulation properties, excellent adhesion to various substrates (such as metals, plastics, and glass), and the ability to withstand thermal cycling and moisture exposure. Electronics applications often require resins that are highly resistant to chemicals and offer good mechanical properties to protect sensitive components from environmental stresses.
The packaging industry uses UV resins for coatings on various types of packaging materials, including paper, plastic, and glass. The main requirement for packaging applications is a quick cure and the ability to provide a smooth, glossy finish. UV coatings on packaging materials must also offer protection against abrasion, moisture, and chemicals to preserve the product’s quality and appearance. In food packaging, resins must comply with safety standards to ensure they do not contaminate the product.

Soft UV resins have a lower hardness and greater flexibility compared to hard UV resins. They are ideal for applications where flexibility and impact resistance are required. Soft UV resins are often used in products that need to absorb mechanical stress without cracking, such as flexible electronics, soft-touch coatings, and protective coatings for fabrics. While they may not offer the same level of scratch resistance as hard resins, they are preferred for applications requiring elasticity and deformation resistance.
Hard UV resins, on the other hand, are characterized by their higher hardness and superior scratch and abrasion resistance. These resins are ideal for applications requiring durability, such as automotive coatings, rigid electronics components, and furniture finishes. Hard UV resins provide a more rigid structure, which makes them suitable for protective coatings where surface integrity is critical. They offer excellent chemical resistance, making them suitable for harsh environments or products exposed to wear and tear.

In the field of 3D printing, UV resins are used to create intricate models, prototypes, and final parts with high precision. These resins are designed to cure under UV light and are available in various formulations to suit different printing technologies, such as SLA (stereolithography) and DLP (digital light processing). In 3D printing, the resin’s curing speed, mechanical properties, and surface finish are essential factors. For functional parts, resins with high toughness and rigidity are preferred, while for artistic or decorative pieces, resins offering high clarity and smooth finishes are often chosen.
· Flexibility: Soft UV resins are used for flexible parts in 3D printing, such as gaskets or soft-touch applications.
· Durability: Hard UV resins are used for functional parts requiring high strength, such as prototypes and end-use parts.
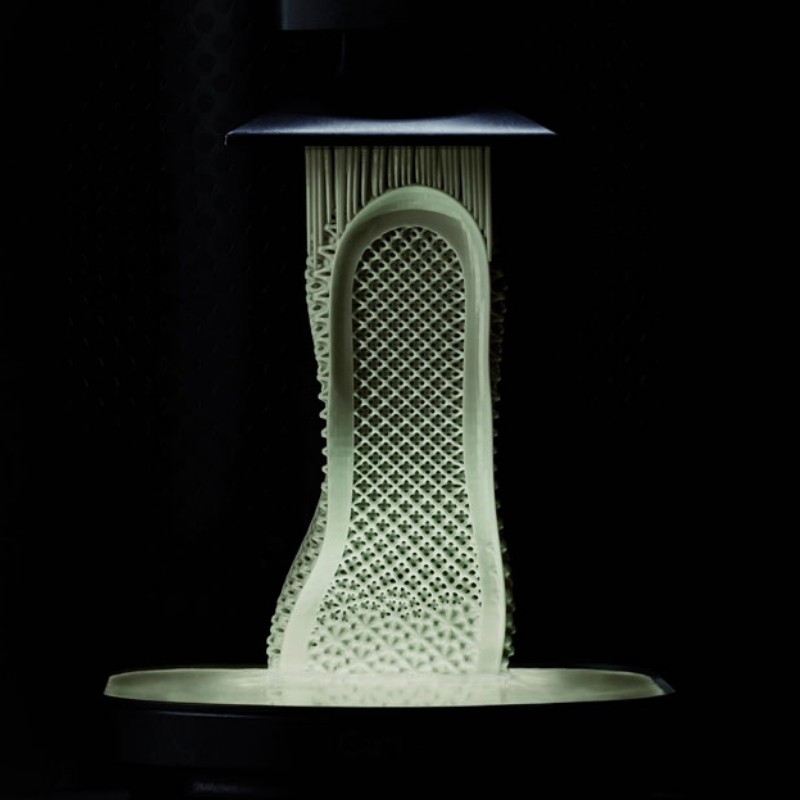

In the medical field, UV resins are used for manufacturing devices such as catheters, implants, and dental products. The resins must comply with strict safety standards to ensure that they are biocompatible, non-toxic, and safe for human use. Medical-grade UV resins must also exhibit excellent mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and stability under various environmental conditions. For instance, in dental applications, UV resins are used for dental restorations like crowns and bridges, where durability and aesthetic appearance are paramount.
· Biocompatibility: Medical UV resins must be non-toxic and able to withstand sterilization processes.
· Precision and Detail: UV resins used in medical applications need to be capable of achieving fine details and smooth finishes for implants or devices that must fit precisely.
Choosing the right UV resin is crucial to achieving the desired performance and quality in any application. Different industries, from automotive and electronics to packaging, have specific requirements for UV resins in terms of adhesion, flexibility, durability, and environmental resistance.
Understanding the differences between soft and hard UV resins is essential for selecting the right material for your project, whether you require flexibility for electronics or hardness for automotive coatings. In high-end applications such as 3D printing and medical devices, UV resins must meet stringent performance standards, including biocompatibility and precision, to ensure their effectiveness. By selecting the appropriate resin, manufacturers can optimize their processes, enhance product performance, and achieve superior results.
#UVResin #UVResinForCrafts #UVResinCoating #FastCuringUVResin #UVResinJewelry #UVResinAdhesive
#HighGlossUVResin #NonYellowingUVResin #CrystalClearUVResin
#UVResinArt


2022-08-03


2025-01-06

